For those involved in the healthcare industry, effective communication is essential to provide high-quality patient care. Clear and concise communication becomes even more crucial when discussing hospital beds, as incorrectly understood verbiage can lead to confusion, delayed treatment, and compromised patient safety. This article aims to decode the intricate jargon related to hospital beds, offering an in-depth understanding of the terminology commonly used in healthcare settings. By familiarizing ourselves with this specialized verbiage, we can enhance communication and ensure seamless operations within hospital environments. 1. Bed Types and Sizes: Understanding the various types and sizes of hospital beds can eliminate confusion while discussing patient requirements. Common terms related to bed types include: a) Standard Bed: A basic type of bed equipped with necessary controls and features for patient use.

.
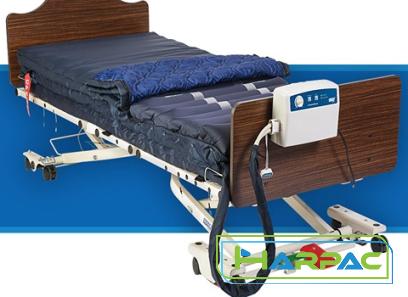
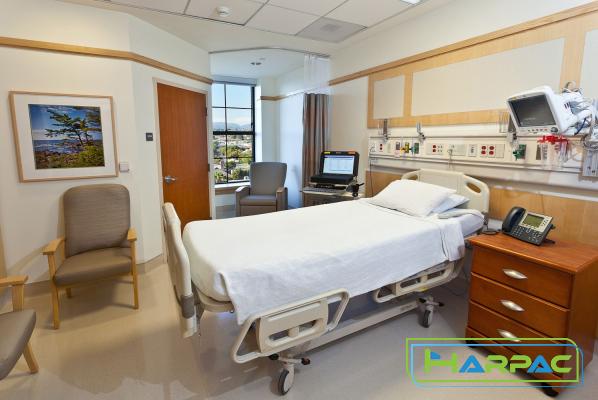 b) Low Bed: A bed designed closer to the ground, minimizing the risk of falls or injury for patients with mobility issues. c) Bariatric Bed: A specialized bed designed to handle higher weight capacities, accommodating overweight or obese patients. d) Air Mattress Bed: A type of bed equipped with an air mattress system that helps prevent pressure ulcers and bedsores. e) Pediatric Bed: Smaller in size, with safety features specifically designed for young patients. 2. Bed Features and Controls: Adequate knowledge of bed features and controls ensures efficient use and patient comfort. Common terminology pertaining to bed features includes: a) Side Rails: Adjustable rails on either side of the bed that provide patient support and prevent falls. b) Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg: These bed positions involve tilting the bed to enable gravity-assisted movement of bodily fluids or organs, either towards the head (Trendelenburg) or toward the feet (Reverse Trendelenburg). c) Fowler’s Position: Elevating the head of the bed to improve patient breathing and reduce the risk of aspiration.
b) Low Bed: A bed designed closer to the ground, minimizing the risk of falls or injury for patients with mobility issues. c) Bariatric Bed: A specialized bed designed to handle higher weight capacities, accommodating overweight or obese patients. d) Air Mattress Bed: A type of bed equipped with an air mattress system that helps prevent pressure ulcers and bedsores. e) Pediatric Bed: Smaller in size, with safety features specifically designed for young patients. 2. Bed Features and Controls: Adequate knowledge of bed features and controls ensures efficient use and patient comfort. Common terminology pertaining to bed features includes: a) Side Rails: Adjustable rails on either side of the bed that provide patient support and prevent falls. b) Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg: These bed positions involve tilting the bed to enable gravity-assisted movement of bodily fluids or organs, either towards the head (Trendelenburg) or toward the feet (Reverse Trendelenburg). c) Fowler’s Position: Elevating the head of the bed to improve patient breathing and reduce the risk of aspiration.
..
 d) Electric Controls: The buttons or panels allowing nurses and patients to adjust bed height, inclination, and other settings. 3. Associated Equipment: Hospital beds are often integrated with various equipment for enhanced patient care and convenience. Familiarize yourself with the following verbiage: a) Overbed Table: A movable table attached to the bed that allows patients to eat, read, or work while remaining in bed. b) IV Pole: A tall pole with hooks or loops designed to hold intravenous (IV) fluids and medications, ensuring safe delivery. c) Bedside Commode: A portable toilet facility that can be placed alongside the bed for patients with limited mobility. 4. Safety Measures: Patient safety is paramount in healthcare settings. Understanding the protective measures associated with beds is crucial for accident prevention and risk management.
d) Electric Controls: The buttons or panels allowing nurses and patients to adjust bed height, inclination, and other settings. 3. Associated Equipment: Hospital beds are often integrated with various equipment for enhanced patient care and convenience. Familiarize yourself with the following verbiage: a) Overbed Table: A movable table attached to the bed that allows patients to eat, read, or work while remaining in bed. b) IV Pole: A tall pole with hooks or loops designed to hold intravenous (IV) fluids and medications, ensuring safe delivery. c) Bedside Commode: A portable toilet facility that can be placed alongside the bed for patients with limited mobility. 4. Safety Measures: Patient safety is paramount in healthcare settings. Understanding the protective measures associated with beds is crucial for accident prevention and risk management.
…
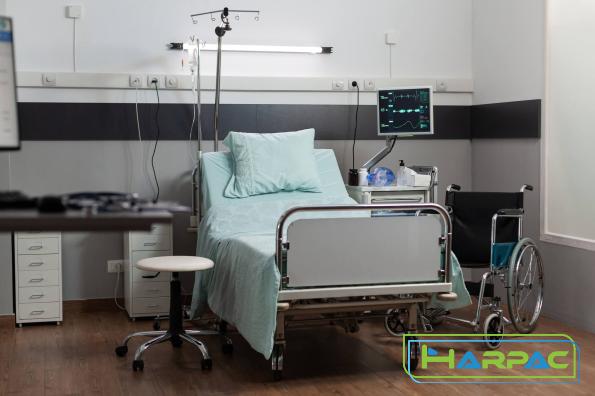 Key terms in this context include: a) Bed Alarms: Electronic alerts triggered when patients attempt to get out of bed unassisted, reducing the risk of falls. b) Bed Exit Sensors: Pressure sensors often installed beneath the mattress that notify healthcare professionals when a patient leaves the bed without assistance. c) CPR Release: A quick-release handle or system allowing healthcare providers to lower the head and foot end of the bed quickly, facilitating Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) efforts. Conclusion: Accurate communication regarding hospital beds is essential for effective patient care, ensuring the well-being and safety of those in need. By familiarizing oneself with commonly used verbiage associated with hospital beds, healthcare professionals can communicate more clearly with their colleagues, patients, and their families. This knowledge promotes collaboration, reduces confusion, and enables seamless operations in hospital environments.
Key terms in this context include: a) Bed Alarms: Electronic alerts triggered when patients attempt to get out of bed unassisted, reducing the risk of falls. b) Bed Exit Sensors: Pressure sensors often installed beneath the mattress that notify healthcare professionals when a patient leaves the bed without assistance. c) CPR Release: A quick-release handle or system allowing healthcare providers to lower the head and foot end of the bed quickly, facilitating Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) efforts. Conclusion: Accurate communication regarding hospital beds is essential for effective patient care, ensuring the well-being and safety of those in need. By familiarizing oneself with commonly used verbiage associated with hospital beds, healthcare professionals can communicate more clearly with their colleagues, patients, and their families. This knowledge promotes collaboration, reduces confusion, and enables seamless operations in hospital environments.








Your comment submitted.