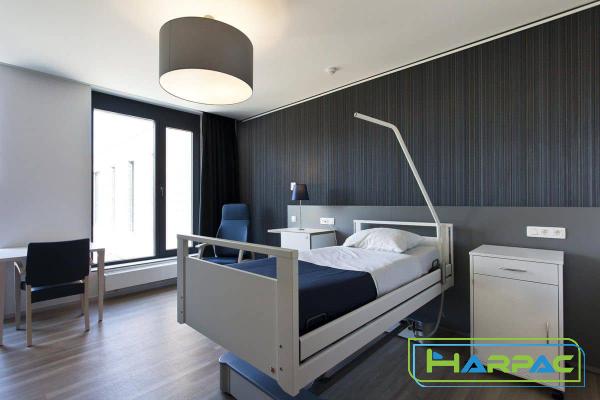
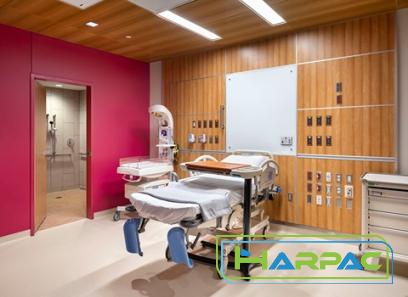
When it comes to purchasing beds for healthcare facilities or personal use, it is crucial to understand the differences between hospital bed sizes and twin beds. While both offer comfort and support, they serve distinct purposes. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of hospital bed size and twin bed, comparing their features, benefits, and their ideal usage scenarios. 1. Hospital Bed Size: Hospital beds are designed to cater to the specific needs of patients in healthcare facilities. They are available in various sizes, but the most common types are twin, full, and bariatric beds. The primary focus of hospital beds is to provide maximum comfort, adaptability, and accessibility to patients who may require medical assistance. Key Features: – Adjustable: Hospital beds can be electrically raised or lowered to accommodate patients’ varying needs and desired positioning. – Side Rails: Most hospital beds come equipped with removable side rails to prevent patients from falling off the bed during their stay.

.
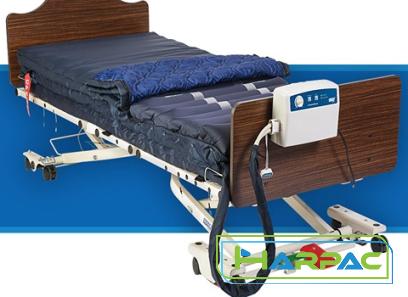
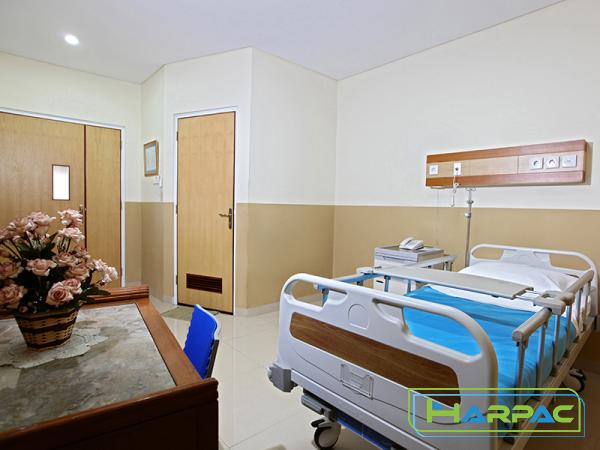 – Mattress Options: Hospital beds often offer specialized mattresses, such as air mattresses for pressure relief or alternating pressure mattresses for preventing bedsores. – Electrical Functions: Some hospital beds have additional features like synchronized movement, trendelenburg positioning, and cardiac chair positioning, all of which cater to specific medical requirements. Benefits: – Enhanced Patient Care: Hospital beds provide a comfortable and secure environment for patients where healthcare professionals can easily monitor and attend to their needs. – Optimal Healthcare Facility Operations: Hospital beds with advanced features can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare providers, enabling them to deliver personalized care. Ideal Usage: – Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers where patients require specialized care and often have limited mobility.
– Mattress Options: Hospital beds often offer specialized mattresses, such as air mattresses for pressure relief or alternating pressure mattresses for preventing bedsores. – Electrical Functions: Some hospital beds have additional features like synchronized movement, trendelenburg positioning, and cardiac chair positioning, all of which cater to specific medical requirements. Benefits: – Enhanced Patient Care: Hospital beds provide a comfortable and secure environment for patients where healthcare professionals can easily monitor and attend to their needs. – Optimal Healthcare Facility Operations: Hospital beds with advanced features can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare providers, enabling them to deliver personalized care. Ideal Usage: – Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers where patients require specialized care and often have limited mobility.
..
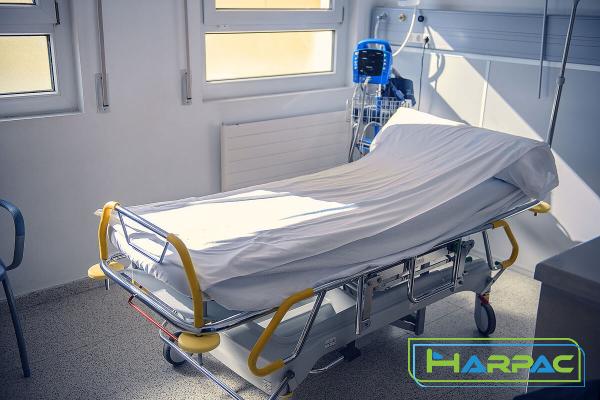 – Home Care: When caring for individuals with chronic illnesses or disabilities who need additional support and assistance. 2. Twin Bed: Twin beds are commonly found in residential settings and are generally designed for individual sleeping arrangements. They are popular choices for children’s bedrooms, guest rooms, and college dormitories. Twin beds are typically smaller in size compared to hospital beds and offer fewer adjustable features. Key Features: – Compact Size: Twin beds are typically narrower and shorter than hospital beds, making them ideal for limited space areas. – Simplicity: Unlike hospital beds, twin beds are straightforward without the addition of specialized functions and features. Benefits: – Space Optimization: Twin beds are perfect for small bedrooms or shared rooms, allowing for more open floor space.
– Home Care: When caring for individuals with chronic illnesses or disabilities who need additional support and assistance. 2. Twin Bed: Twin beds are commonly found in residential settings and are generally designed for individual sleeping arrangements. They are popular choices for children’s bedrooms, guest rooms, and college dormitories. Twin beds are typically smaller in size compared to hospital beds and offer fewer adjustable features. Key Features: – Compact Size: Twin beds are typically narrower and shorter than hospital beds, making them ideal for limited space areas. – Simplicity: Unlike hospital beds, twin beds are straightforward without the addition of specialized functions and features. Benefits: – Space Optimization: Twin beds are perfect for small bedrooms or shared rooms, allowing for more open floor space.
…
 – Cost-Effective: Compared to hospital beds, twin beds are usually more affordable, making them a practical choice for budget-conscious individuals. Ideal Usage: – Residential Settings: Children’s bedrooms, guest rooms, small apartments, college dormitories, and any space where individual sleep arrangements are required. Conclusion: Choosing between a hospital bed and a twin bed involves understanding the specific needs and requirements of the user. While hospital beds offer advanced functions and accommodations designed to enhance patient care and medical support, twin beds serve well in residential settings where simplicity and space optimization are key factors. By considering the features, benefits, and intended usage, individuals and healthcare facility managers can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate bed solution for their specific needs.
– Cost-Effective: Compared to hospital beds, twin beds are usually more affordable, making them a practical choice for budget-conscious individuals. Ideal Usage: – Residential Settings: Children’s bedrooms, guest rooms, small apartments, college dormitories, and any space where individual sleep arrangements are required. Conclusion: Choosing between a hospital bed and a twin bed involves understanding the specific needs and requirements of the user. While hospital beds offer advanced functions and accommodations designed to enhance patient care and medical support, twin beds serve well in residential settings where simplicity and space optimization are key factors. By considering the features, benefits, and intended usage, individuals and healthcare facility managers can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate bed solution for their specific needs.








Your comment submitted.