Rotating hospital beds have revolutionized patient care by providing a dynamic and adaptable solution for medical facilities. These beds offer a range of movement options, allowing patients to reposition themselves without assistance and reducing the risk of pressure ulcers and other complications. In this article, we explore different types of rotating hospital beds and their numerous benefits. 1. Rotating Low Air Loss Beds: One type of rotating hospital bed is the rotating low air loss bed. These beds not only rotate but also utilize a specialized air mattress system. The rotatable feature ensures that patients can reposition themselves easily, preventing immobilization and promoting independence.
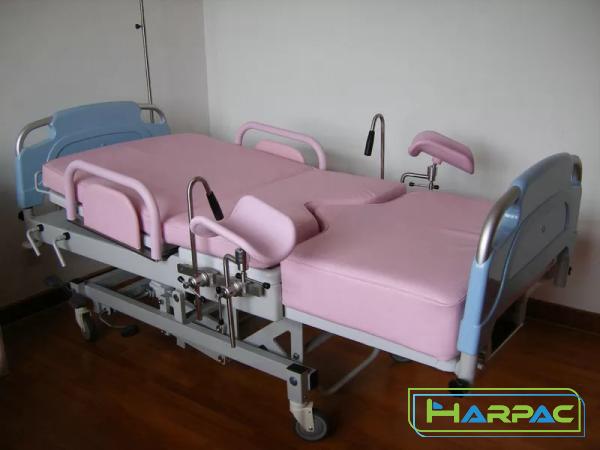
.
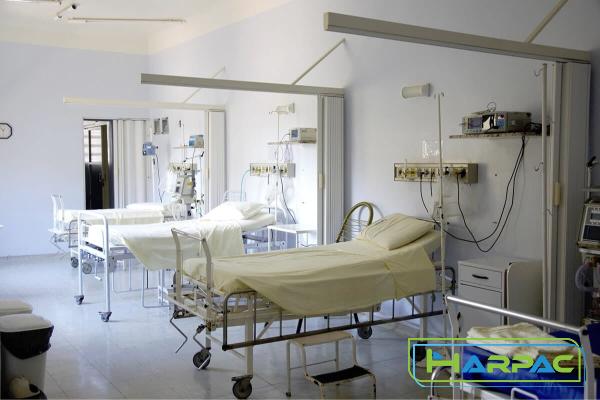 The low air loss technology helps prevent and heal pressure ulcers by reducing moisture and heat buildup. 2. Rotational Therapy Beds: Rotational therapy beds are designed to assist patients with mobility restrictions, such as those experiencing spinal cord injuries or neuromuscular disorders. These beds gently rotate the patient at programmed intervals, helping to maintain joint integrity, promote circulation, and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal issues caused by immobility. 3. Lateral Rotation Beds: Lateral rotation beds are particularly beneficial for patients with limited mobility. These beds slowly rotate patients from side to side, replicating the natural movement experienced while turning in bed. This gentle motion helps with secretion drainage, promotes lung expansion, and improves overall comfort for patients who are unable to reposition themselves independently.
The low air loss technology helps prevent and heal pressure ulcers by reducing moisture and heat buildup. 2. Rotational Therapy Beds: Rotational therapy beds are designed to assist patients with mobility restrictions, such as those experiencing spinal cord injuries or neuromuscular disorders. These beds gently rotate the patient at programmed intervals, helping to maintain joint integrity, promote circulation, and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal issues caused by immobility. 3. Lateral Rotation Beds: Lateral rotation beds are particularly beneficial for patients with limited mobility. These beds slowly rotate patients from side to side, replicating the natural movement experienced while turning in bed. This gentle motion helps with secretion drainage, promotes lung expansion, and improves overall comfort for patients who are unable to reposition themselves independently.
..
 4. Bariatric Rotating Beds: Designed for patients with higher weight capacities, bariatric rotating beds are specially built to accommodate larger individuals. These beds incorporate rotating features along with reinforced frames, wider sleeping surfaces, and strong support systems. Bariatric rotating beds improve patient safety, ease of care, and allow for efficient patient handling and repositioning. Benefits of Rotating Hospital Beds: a) Pressure Ulcer Prevention: The ability to self-reposition reduces the risk of developing pressure ulcers, a common concern for immobile patients. Rotating beds also distribute pressure more evenly, minimizing the risk of tissue damage. b) Improved Circulation: Regular repositioning promotes blood flow and reduces the likelihood of blood pooling and related complications like deep vein thrombosis. c) Respiratory Health: Rotational beds aid in lung expansion and secretion drainage, reducing the risk of pulmonary complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis.
4. Bariatric Rotating Beds: Designed for patients with higher weight capacities, bariatric rotating beds are specially built to accommodate larger individuals. These beds incorporate rotating features along with reinforced frames, wider sleeping surfaces, and strong support systems. Bariatric rotating beds improve patient safety, ease of care, and allow for efficient patient handling and repositioning. Benefits of Rotating Hospital Beds: a) Pressure Ulcer Prevention: The ability to self-reposition reduces the risk of developing pressure ulcers, a common concern for immobile patients. Rotating beds also distribute pressure more evenly, minimizing the risk of tissue damage. b) Improved Circulation: Regular repositioning promotes blood flow and reduces the likelihood of blood pooling and related complications like deep vein thrombosis. c) Respiratory Health: Rotational beds aid in lung expansion and secretion drainage, reducing the risk of pulmonary complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis.
…
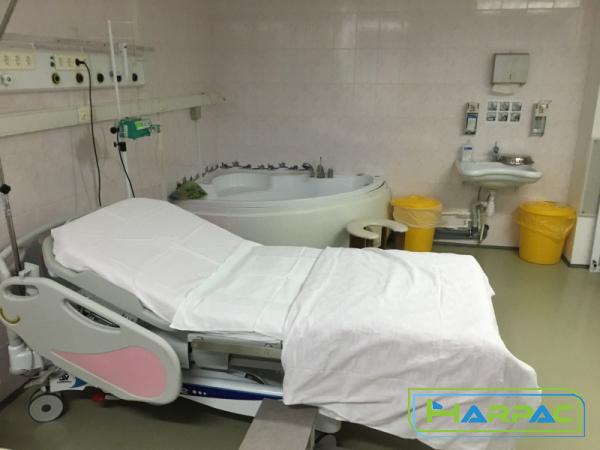 d) Patient Comfort: The ability to independently adjust positions enhances comfort, mitigates muscle stiffness, and promotes better sleep quality. e) Caregiver Assistance: Rotating beds reduce the physical strain on healthcare professionals by enabling patients to move themselves in the bed, thus decreasing the need for constant repositioning. Conclusion: Rotating hospital beds have become indispensable in modern healthcare settings, offering numerous benefits to both patients and healthcare providers. With a wide range of options available, hospitals can choose the type of rotating bed that best suits their patients’ needs. Whether it’s preventing pressure ulcers, improving circulation, or enhancing patient comfort, rotating beds play a vital role in delivering quality care while promoting patient independence and well-being.
d) Patient Comfort: The ability to independently adjust positions enhances comfort, mitigates muscle stiffness, and promotes better sleep quality. e) Caregiver Assistance: Rotating beds reduce the physical strain on healthcare professionals by enabling patients to move themselves in the bed, thus decreasing the need for constant repositioning. Conclusion: Rotating hospital beds have become indispensable in modern healthcare settings, offering numerous benefits to both patients and healthcare providers. With a wide range of options available, hospitals can choose the type of rotating bed that best suits their patients’ needs. Whether it’s preventing pressure ulcers, improving circulation, or enhancing patient comfort, rotating beds play a vital role in delivering quality care while promoting patient independence and well-being.
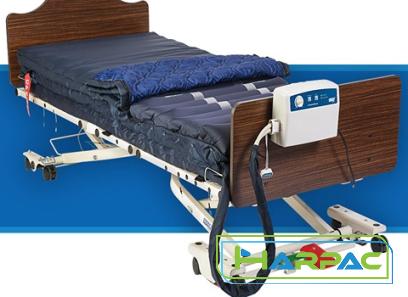








Your comment submitted.